Galaxy Discovery Sheds New Light on How Structures Formed 10 Billion Years Ago
What old light can tell researchers about how galaxies form.
— -- New clues have been discovered in the distant universe that shed light on how galaxies formed.
The universe is believed to be 13.8 billion years old and is home to an estimated 100 billion galaxies comprised of stars, gas and dust. However, researchers are unsure how those giant clusters came to be.
In order to capture light from the early universe, the European Space Agency's Planck telescope used cosmic microwave background signals to create a map of the radiation left by the Big Bang.
The Herschel telescope was then used to zoom in on some of the clusters that were captured by the Planck telescope, allowing researchers to examine what are believed to be precursors to galaxies.
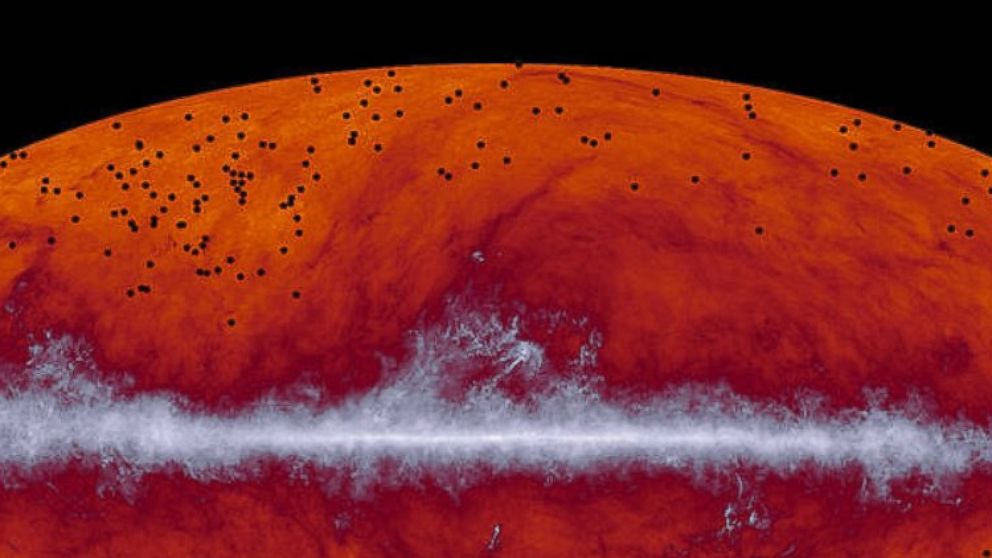
The oval projection in the above photo is the entire sky, while the emission from Earth's home galaxy, the Milky Way, is shown as the band stretching across the center. The black dots are believed to be newly discovered clusters.
"Finding so many intensely star-forming, dust galaxies in such concentrated groups was a huge surprise," Hervé Dole, lead author of the study that will be published in the journal Astronomy and Astrophysics on Tuesday said, according to NASA. "We think this is a missing piece of cosmological structure formation."
While stars and galaxies were abundant in the early universe, they would collapse under the weight of gravity and trigger the creation of new stars and galaxies, according to NASA.
The findings show that the galaxies from the early universe have been able to create stars from gas and dust at a rate of as many 1,500 solar masses per year. The Milky Way today averages about one solar mass per year, according to the European Space Agency, meaning that about one star with the weight of our sun is created from dust and gas every year.
Astrophysicists haven't yet determined the age of the distant clusters. However, they believe they are likely the closest evidence that has been found to the enormous galaxies seen today closer to our own.




