Increasingly warming planet jeopardizes human health, major report warns
Temperature increases have been associated with a decline in mental health.
As temperatures continue to increase worldwide, so do profound impacts on our health, including our mental health, according to a major report by almost 100 experts, including the World Health Organization, recently published by the Lancet Countdown. This 7th annual report builds on prior reports, echoing a dire warning about the health consequences of a warming planet.
While some impacts of record-high temperatures may be more expected – such as increased illness due to exposure to heat waves and extremely high temperatures – other impacts, such as increased risk of mental health problems, and increased spread of infections are less obvious effects that can have global impacts, the report said.
According to the report, severe temperature increases, and heat waves have been associated with a decline in mental health and increased suicidality.
"Climate change affects the mental health of people through a variety of different pathways," Dr. Marina Romanello, the executive director of the Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change report, told ABC News.
"Some are more evident and easily attributable, such as the profound mental health impacts of extreme weather event-related disasters," Romanello said. "However, the mental health impacts of climate change can also come, for example, from extreme heat exposure, which has been associated in the literature with increased interpersonal violence, crime, and self-harm."

With climate change, young people in particular have been more susceptible to depression, anxiety, substance use and issues with sleep, the report said.
"Eighty-four percent of young people, are moderately to extremely anxious about climate change," Dr. Elizabeth Haase, the chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s Committee on Climate Change and Mental Health, told ABC News. "Along with the continued stresses that follow extreme weather come more drug and alcohol abuse, more child abuse and domestic violence, more poverty, poorer diets, increased homelessness, fractured families and communities."
In addition to these profound mental health impacts, the report details how increased temperatures are putting our physical health at risk.
Heat-related deaths in those older than 65 increased by almost 70% from 2000-2004 to 2017-2021. Exposure to extremely high temperatures is associated with heat stroke, kidney injury, and worsening of existing heart and lung diseases. With increases in temperatures, there is also increased spread and survival of some infectious diseases, resulting in an overall increased risk of infectious disease outbreaks.
The main cause of climate change has been the use of fossil fuels, which also come with other risks to our health. Fossil fuels use has also resulted in a worsening of air pollution, which contributed to over 1 million deaths in 2020, according to the report.
"The accelerating health impact of climate change has become increasingly apparent. It is having devastating health effects," Dr. Georges Benjamin, executive director of the American Public Health Association, told ABC News. "The new Lancet report further documents the devastation climate change is causing on the global population."
With all these possible health impacts – is our health system, which has recently already been stretched thin with the COVID-19 pandemic, ready to deal with these possible consequences? Not quite. "The health sector’s response to date has been inadequate and must be dramatically increased because the global health is in immediate peril," Benjamin said.
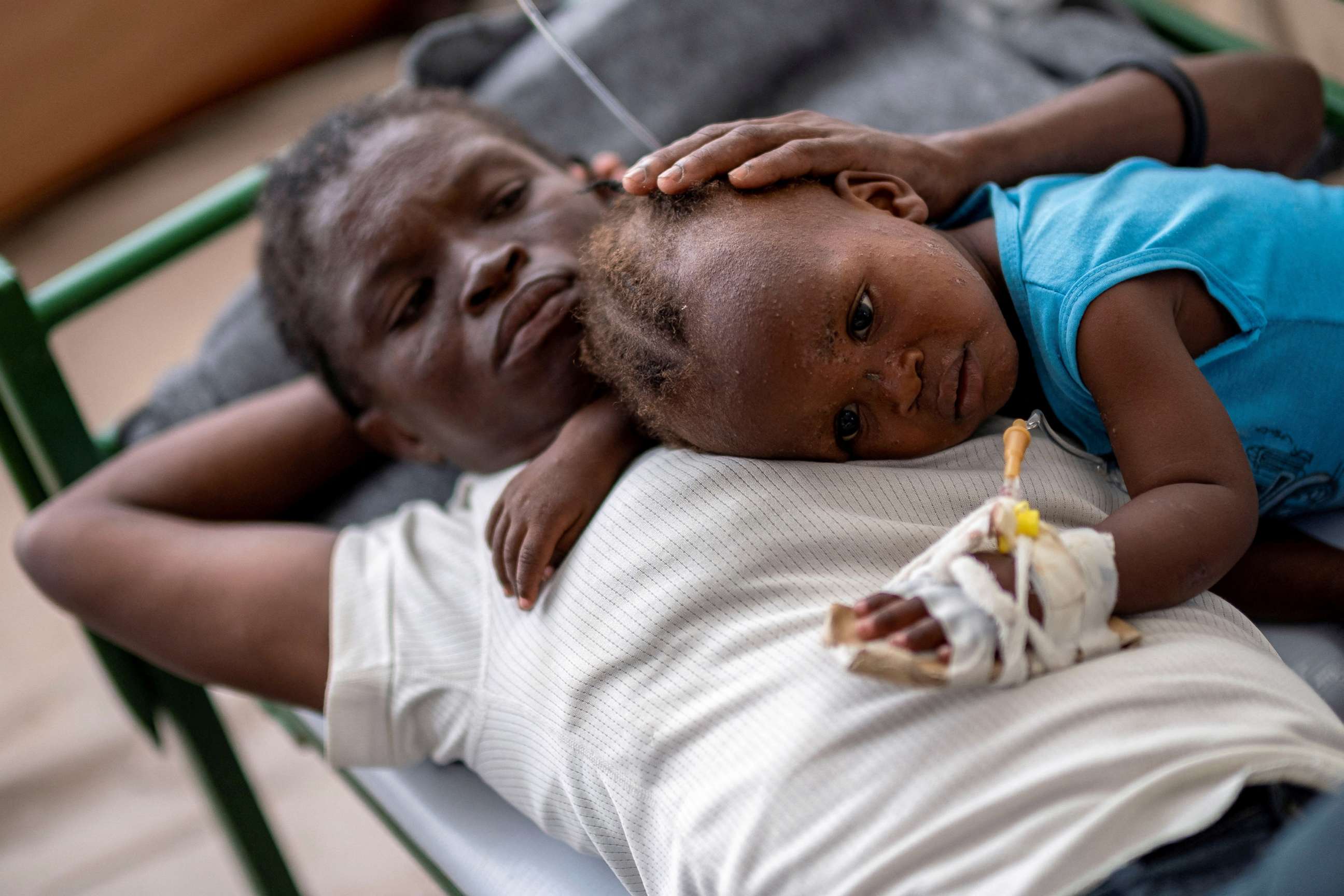
Society may be even less prepared to deal with the mental health impacts of climate change, scientists warn. Just last December, U.S. Surgeon General Dr. Vivek Murthy issued an advisory on the youth mental health crisis.
With recent large increases in youth requiring mental health services, our already understaffed mental health care system has been further stretched thin and unable to meet this need. And climate change is expected to further increase the need for these services.
According to the Lancet report, only a minority of countries have considered the mental health impacts of climate change in their action plans and only about one in every four countries report having a program that incorporates mental health into their disaster preparedness programs.
"This clearly shows that we are not preparing to cope, and minimize, the expected increase in mental health impacts from the changing climate," Romanello said.
Anna Yegiants, MD, MPH is a resident physician in psychiatry, and a member of the ABC News Medical Unit.




