5 things to know about the Iran protests
At least 21 people have been killed in six days of mass protests sweeping Iran.
— -- At least 21 people have died in six days of mass protests sweeping Iran, state media reported.
Among them were six protesters who died in clashes with authorities while trying to break into a police station in the town of Qahdarijan in central Isfahan province Monday night, Iranian state television reported.
Hundreds of people have also been arrested in Iran's capital in recent days, according to Ali Asghar Naserbakht, the deputy governor of Tehran province.
The demonstrations, which began in the northeastern city of Mashhad last week, are the biggest challenge to Iran's Islamic Republic since mass protests erupted over a disputed election in 2009. The ongoing unrest stemmed from grievances over economic hardships and has since expanded into a nationwide show of dissent against the country's leadership.
Here are five things to know about the Iran protests:
1. The key players
Two main political factions have controlled post-revolutionary Iran: the reformists and the conservatives. The reformists, represented by former President Mohammad Khatami, support gradual changes to make Iran more free and democratic. The conservatives, who favor Iran's supreme leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, support maintaining and preserving the authoritarian status quo.
Iranian President Hassan Rouhani won the 2013 election as a moderate backed by reformists, promising greater freedoms for Iranians and detente abroad after years of global sanctions against the country amid two terms of a conservative presidency. Rouhani led Iran through two years of negotiations with the United States, the United Kingdom, Russia, France, Germany and China that resulted in a historic deal in 2015, under which Iran agreed to limit its controversial nuclear development program in return for sanctions relief.
Rouhani, again backed by reformists, won re-election in a landslide vote in 2017. The president vowed to stabilize the economy and further improve international relations during his second term. But he has faced numerous obstacles to fulfilling those promises.
Among those challenges were thousands of unlicensed credit and finance institutions in Iran that had flourished during the two terms of Rouhani's predecessor. These institutions had lured millions of customers, hoping to make money amid a stagnant economy by offering high interest rates on deposits in the Iranian currency. But because of extensive corruption, many of them collapsed and went bankrupt.
Countless Iranians lost their savings, leading to a series of small protests across the country in recent months.
Sanctions were eased after the nuclear deal, but Rouhani decided to amend tax regulations to compensate for Iran's shrinking oil revenue. Iranians have used smartphones and social networks to closely monitor the policy move since the president submitted a draft 2018 budget to parliament Dec. 10.
While proposing the budget plan, Rouhani acknowledged that six financial institutions used to control 25 percent of the country's currency market and that he struggled to curb the corruption. The budget proposal also revealed plans to increase the price of fuel, as well as the allocation of hundreds of millions of dollars to the clergy and the hardliner institutions under their control, while the government would slash spending for infrastructure projects and cash subsidies.
The budget plan is still under review.
Many Iranians took to social media to express discontent over inequality and to demand that the government devote more money and attention to the country's low-income population, rather than the clergy. Rouhani openly said he supported the criticism and urged Iranians to keep pushing for their demands.
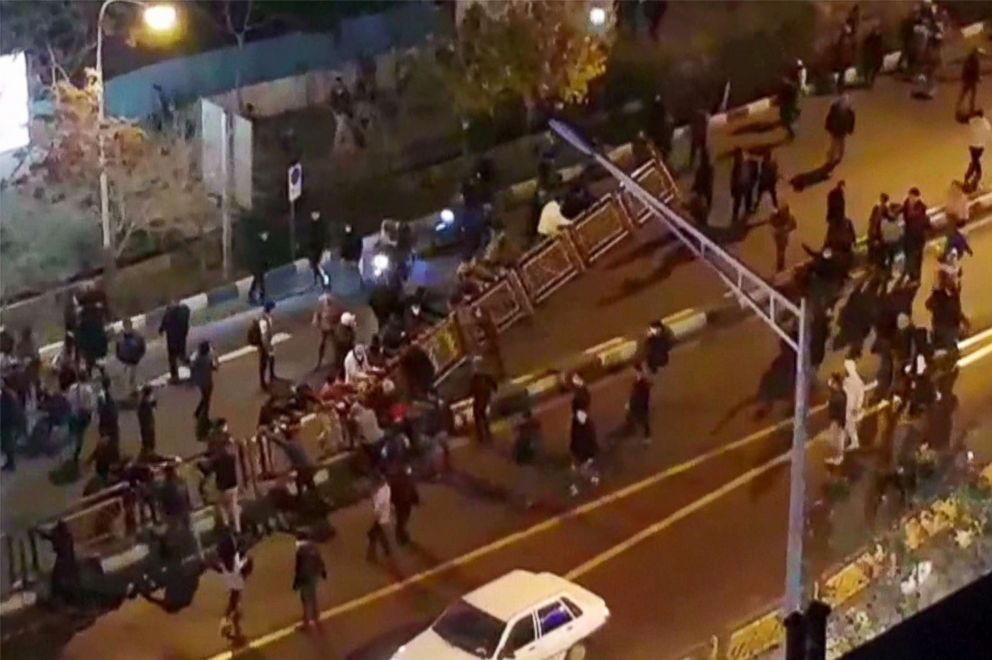
2. How the protests started
On Dec. 28, about two weeks after the budget proposal, an anti-government protest was held in Mashhad, Iran's second-largest city and hometown of the supreme leader. The demonstration was reportedly organized by conservatives to try to weaken Rouhani because they do not agree with his domestic and international policies that endangered the safe haven that years of sanctions had provided them for their allegedly corrupt financial activities.
The demonstrators took to the streets, chanting against high prices and shouting slogans against Rouhani and his government. But other protesters soon joined in and started demanding a wholesale change in the entire system.
Police ultimately quashed the protest, but word of the demonstration quickly spread on social media and encouraged people in other cities to organize.
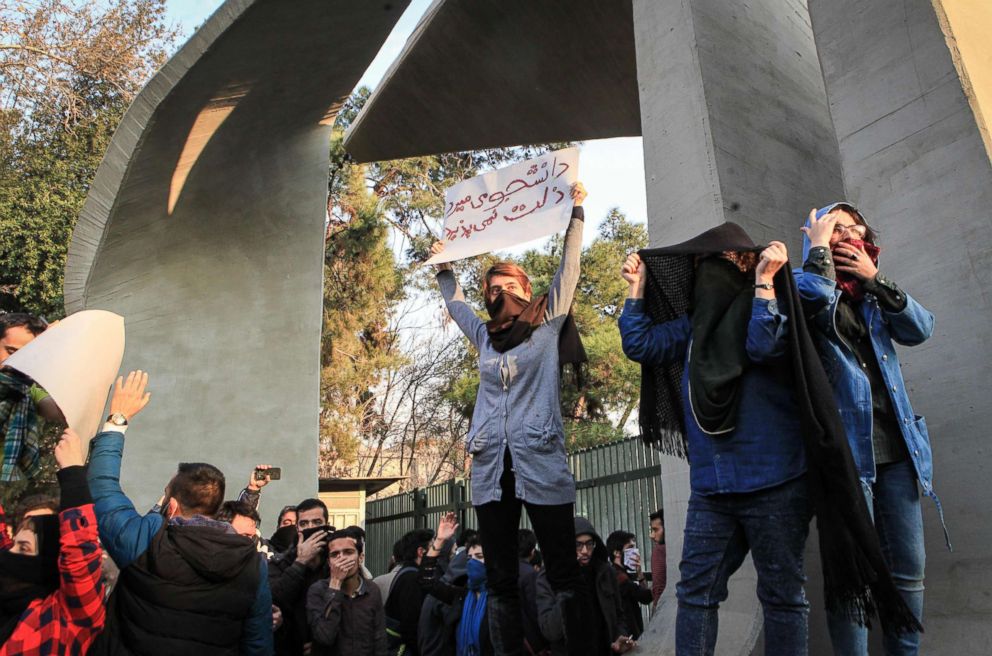

3. How the protests have evolved
The next day, protests ignited in other cities across Iran, including the capital, Tehran.
But the largest protest that day formed in Kermanshah, the main city in a western region where a magnitude-7.3 earthquake had killed hundreds of people in November. There, hundreds of protesters poured into the streets, shouting slogans that ranged from expressing frustration over rising prices to questioning Iran's foreign policy.
Some of the demonstrators in Kermanshah called for the release of political prisoners, economic reforms and greater social freedoms. Some also protested against Iran’s longstanding support for the Palestinians, shouting, “No Gaza, no Lebanon. I offer my life for Iran.”
Police eventually intervened in the protest.
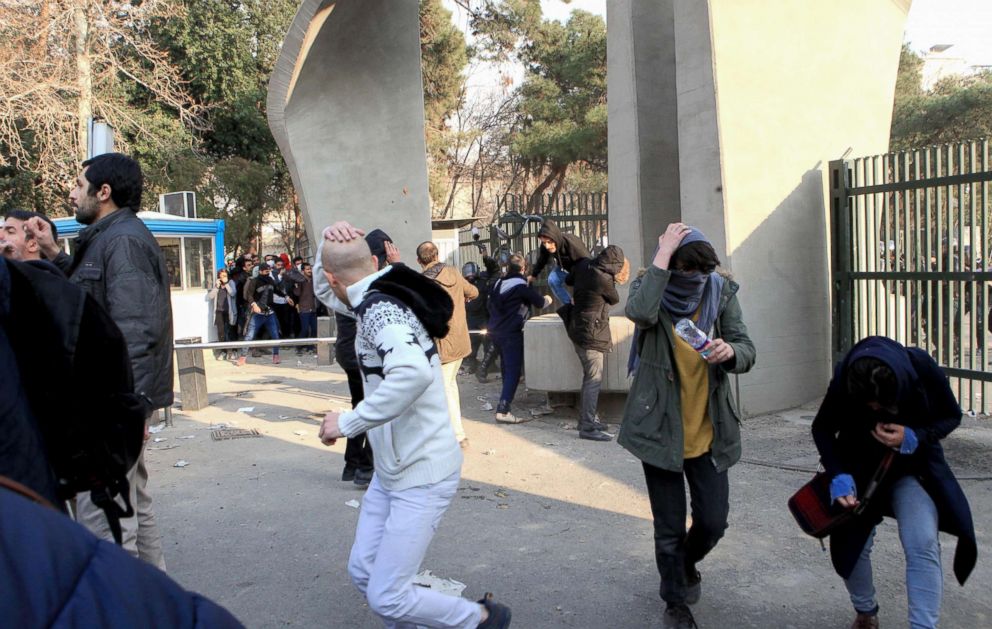
In other cities in the following days, however, protests became more violent with demonstrators setting trash bins ablaze, shattering windows of banks and setting fire to some religious schools and temples.
Maj. Gen. Mohammad Ali Jafari, the commander of the Iranian Revolutionary Guard Corps, has estimated that the largest single gathering in the past six days had 1,500 protesters, while the total number of protesters nationwide was about 15,000. Jafari said today would be the last day of the protests.
One protester, who spoke to ABC News on condition of anonymity, said she voted for Rouhani and is frustrated by the lack of any real change.
"We told ourselves that he is our last hope," the protester said in a telephone interview Tuesday. "But, unfortunately, now neither reformists nor conservatives gave us any hope or motivation.
"I'd like to live in a free country, a country with no pressure," she added.
The protester cited the country's economic turmoil and livelihood concerns as her main motivators, as well as ideological, political and social issues. She said she wants a referendum to change the theocratic system and she believes protesting is the only way to achieve that.
"Can you really think of any other method? Can we do anything else?" she said.
But some reformists and commentators believe it's a sensitive time for an uprising and any move that could destabilize the country might push it over the edge into civil war, like Syria.
Iranian blogger Pooria Astaraky wrote on Twitter in Farsi, “They want to play the same game as they did to Syria. Do you remember that some years ago people thought ISIS was Syrian people’s army for liberty?”
The anti-government protests have sparked counterdemonstrations. Tens of thousands of people across the country partook in rallies to show support for the theocratic system and to protest the violence in recent days, Iranian state television reported today. Pro-system demonstrators, mainly supporting the supreme leader and conservatives, in dozens of cities and towns were seen waving Iranian flags and carrying signs, some showing U.S. President Donald Trump's face covered with a bright red "X."

4. How leaders are reacting
After three days of silence, Rouhani acknowledged the nationwide unrest in remarks to members of parliament Monday, describing it as "an opportunity" rather than "a threat." Still, he said violence and damage to public property would not be tolerated.
“I believe what has happened in the past few days is an opportunity despite it looking like a threat. We have to find out the problem," the president said. "People have not come to the street for merely economic problems. They are not just asking for bread and water.
"We have to listen. We have to make it an opportunity and find a solution," he added.
On the other side of Iran's political spectrum, the supreme leader on Tuesday accused "enemies of Iran" of meddling in the ongoing protests.
"Look at the recent days’ incidents," Khamenei said while visiting families. "All those who are at odds with the Islamic Republic have utilized various means, including money, weapons, politics and (the) intelligence apparatus, to create problems for the Islamic system, the Islamic Republic and the Islamic Revolution."
Khamenei avoided naming any foreign countries, but said he would elaborate in the coming days. He also warned of an enemy “waiting for an opportunity, for a crack through which it can infiltrate.”
“Look at the recent days’ incidents,” he said. “All those who are at odds with the Islamic Republic have utilized various means, including money, weapons, politics and [the] intelligence apparatus, to create problems for the Islamic system, the Islamic Republic and the Islamic Revolution.”
Meanwhile, Iranian Foreign Minister Mohammad Javad Zarif Tuesday tweeted that "Iran's security and stability depend on its own people," but warned against violent "infiltrators."
Zarif also took aim at Trump and U.S. foreign policy.
Trump has been tweeting extensively in support of the Iran protests. The U.S. president Monday tweeted, "Iran is failing at every level despite the terrible deal made with them by the Obama Administration. The great Iranian people have been repressed for many years. They are hungry for food & for freedom. Along with human rights, the wealth of Iran is being looted. TIME FOR CHANGE!"
Trump tweeted Tuesday, "The people of Iran are finally acting against the brutal and corrupt Iranian regime. All of the money that President Obama so foolishly gave them went into terrorism and into their 'pockets.' The people have little food, big inflation and no human rights. The U.S. is watching!"
Trump tweeted about the Iran protests again today, saying, "Such respect for the people of Iran as they take back their corrupt government. You will see great support from the United States at the appropriate time!"
Interpreting Trump's latest tweet, some Iranians speculated on Twitter that the U.S. president plans to use the unrest as a means to push Congress to pull out of the Iran nuclear deal.
5. What's next
Abbas Abdi, an influential reformist sociologist in Iran, said he believes the protests will end soon because of no comprehensive support from the middle class.
"It does not mean the middle class supports the system," Abdi told ABC News in a telephone interview Monday. "They do have serious criticism to the system, but they do not negotiate over the integrity of their country. They are against this kind of riots because it will not benefit anyone."
The ongoing protests are not being taken as seriously as the so-called Green Movement of 2009, Abdi said, when millions of Iranians poured into the streets to protest the re-election of President Mahmoud Ahmadinejad. And while the protesters in 2009 were largely peaceful, the latest demonstrations have been violent and deadly, which, Abdi said, will lead Iranian authorities to extinguish them quickly.
"But ending the riots will not mean the problem is solved," Abdi added. "It will be there and will not be solved unless the judiciary, the state-run media and the Guardian Council -- which is responsible for supervising the elections -- accept to implement real reforms in midterm and long-term reforms."
ABC News' Afshin Abtahi contributed to this report.




