Want $18,000 to Stay in Bed? Try NASA
NASA is looking for participants willing to stay off their feet. Specifically they're looking for research subjects willing to remain on a special tilted bed for 70 straight days.
But full participation in a bed rest study isn't exactly easy. Subjects will not be able to get out of bed for any reason and have to pass a modified Air Force Class Physical, which includes an electrocardiogram, a drug and alcohol screening, and infectious disease screening.
According to Forbes.com, participants who complete the study will make $18,000 or $1,200 per week.
Private Company Rockets Toward Space Station
Beth Ann Shriber, who participated in a 2006 study, said the monotony of remaining in bed all day, every day, can take its toll psychologically.
"You don't have to do anything but lie here," Shriber said in an article on NASA.gov. "I would say it's more about enduring."
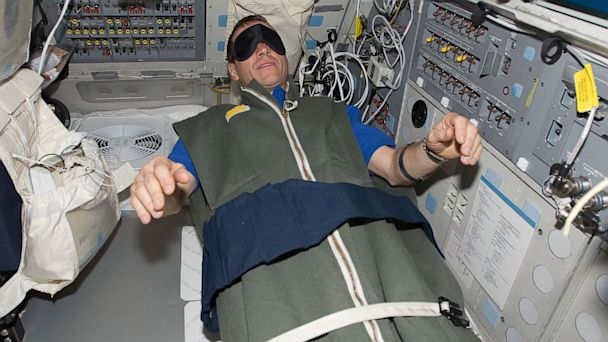
The current study is designed to examine the longterm effects of weightlessness on astronauts' bodies. To simulate space the study subjects will lie on a specially designed bed that is tilted slightly.
In space there is no gravity to keep fluid from traveling towards the top of the body, so study participants lie with their head slightly lower than their feet. Certain subjects will be able to periodically exercise on specially designed equipment like a vertical treadmill.
NASA Craft Finds No Hint of Methane on Mars
Simply by lying in bed the participants will experience a host of physical effect including atrophying muscles and a decrease of bone density. In addition, a person's overall fitness can decrease, since their hearts don't have to work as hard to pump blood.
In spite of the challenges, some participants have been interested in repeating the experiment.
"Some people are really interested in the science return and love helping NASA," John Neigut, a researcher with the NASA Flight Analogs Project, told the Houston Chronicle. "We have numerous repeat requests for people to come back to the study."
The study will be based out of NASA's Human Test Subject Facility at the University of Texas Medical Branch medical center in Galveston, Texas. After participating in the experiment, subjects will have a two-week period to recuperate.